This is “Writing Essays: From Start to Finish”, chapter 8 from the book English for Business Success (v. 1.0). For details on it (including licensing), click here.
For more information on the source of this book, or why it is available for free, please see the project's home page. You can browse or download additional books there. To download a .zip file containing this book to use offline, simply click here.
Chapter 8 Writing Essays: From Start to Finish
8.1 Developing a Strong, Clear Thesis Statement
Learning Objectives
- Develop a strong, clear thesis statement with the proper elements.
- Revise your thesis statement.
Have you ever known a person who was not very good at telling stories? You probably had trouble following his train of thought as he jumped around from point to point, either being too brief in places that needed further explanation or providing too many details on a meaningless element. Maybe he told the end of the story first, then moved to the beginning and later added details to the middle. His ideas were probably scattered, and the story did not flow very well. When the story was over, you probably had many questions.
Just as a personal anecdote can be a disorganized mess, an essay can fall into the same trap of being out of order and confusing. That is why writers need a thesis statementA sentence that presents the controlling idea of an essay. A thesis statement is often one sentence long and states the writer’s point of view. to provide a specific focus for their essay and to organize what they are about to discuss in the body.
Just like a topic sentence summarizes a single paragraph, the thesis statement summarizes an entire essay. It tells the reader the point you want to make in your essay, while the essay itself supports that point. It is like a signpost that signals the essay’s destination. You should form your thesis before you begin to organize an essay, but you may find that it needs revision as the essay develops.
Elements of a Thesis Statement
For every essay you write, you must focus on a central idea. This idea stems from a topic you have chosen or been assigned or from a question your teacher has asked. It is not enough merely to discuss a general topic or simply answer a question with a yes or no. You have to form a specific opinion, and then articulate that into a controlling ideaThe main idea that guides the content of an essay; the idea upon which a thesis statement is built.—the main idea upon which you build your thesis.
Remember that a thesis is not the topic itself, but rather your interpretation of the question or subject. For whatever topic your professor gives you, you must ask yourself, “What do I want to say about it?” Asking and then answering this question is vital to forming a thesis that is precise, forceful and confident.
A thesis is one sentence long and appears toward the end of your introduction. It is specific and focuses on one to three points of a single idea—points that are able to be demonstrated in the body. It forecasts the content of the essay and suggests how you will organize your information. Remember that a thesis statement does not summarize an issue but rather dissects it.
A Strong Thesis Statement
A strong thesis statement contains the following qualities.
Specificity. A thesis statement must concentrate on a specific area of a general topic. As you may recall, the creation of a thesis statement begins when you choose a broad subject and then narrow down its parts until you pinpoint a specific aspect of that topic. For example, health care is a broad topic, but a proper thesis statement would focus on a specific area of that topic, such as options for individuals without health care coverage.
Precision. A strong thesis statement must be precise enough to allow for a coherent argument and to remain focused on the topic. If the specific topic is options for individuals without health care coverage, then your precise thesis statement must make an exact claim about it, such as that limited options exist for those who are uninsured by their employers. You must further pinpoint what you are going to discuss regarding these limited effects, such as whom they affect and what the cause is.
Ability to be argued. A thesis statement must present a relevant and specific argument. A factual statement often is not considered arguable. Be sure your thesis statement contains a point of view that can be supported with evidence.
Ability to be demonstrated. For any claim you make in your thesis, you must be able to provide reasons and examples for your opinion. You can rely on personal observations in order to do this, or you can consult outside sources to demonstrate that what you assert is valid. A worthy argument is backed by examples and details.
Forcefulness. A thesis statement that is forceful shows readers that you are, in fact, making an argument. The tone is assertive and takes a stance that others might oppose.
Confidence. In addition to using force in your thesis statement, you must also use confidence in your claim. Phrases such as I feel or I believe actually weaken the readers’ sense of your confidence because these phrases imply that you are the only person who feels the way you do. In other words, your stance has insufficient backing. Taking an authoritative stance on the matter persuades your readers to have faith in your argument and open their minds to what you have to say.
Tip
Even in a personal essay that allows the use of first person, your thesis should not contain phrases such as in my opinion or I believe. These statements reduce your credibility and weaken your argument. Your opinion is more convincing when you use a firm attitude.
Exercise 1
On a separate sheet of paper, write a thesis statement for each of the following topics. Remember to make each statement specific, precise, demonstrable, forceful and confident.
Topics
- Texting while driving
- The legal drinking age in the United States
- Steroid use among professional athletes
- Abortion
- Racism
Examples of Appropriate Thesis Statements
Each of the following thesis statements meets several of the following requirements:
- Specificity
- Precision
- Ability to be argued
- Ability to be demonstrated
- Forcefulness
- Confidence
- The societal and personal struggles of Troy Maxon in the play Fences symbolize the challenge of black males who lived through segregation and integration in the United States.
- Closing all American borders for a period of five years is one solution that will tackle illegal immigration.
- Shakespeare’s use of dramatic irony in Romeo and Juliet spoils the outcome for the audience and weakens the plot.
- J. D. Salinger’s character in Catcher in the Rye, Holden Caulfield, is a confused rebel who voices his disgust with phonies, yet in an effort to protect himself, he acts like a phony on many occasions.
- Compared to an absolute divorce, no-fault divorce is less expensive, promotes fairer settlements, and reflects a more realistic view of the causes for marital breakdown.
- Exposing children from an early age to the dangers of drug abuse is a sure method of preventing future drug addicts.
- In today’s crumbling job market, a high school diploma is not significant enough education to land a stable, lucrative job.
Tip
You can find thesis statements in many places, such as in the news; in the opinions of friends, coworkers or teachers; and even in songs you hear on the radio. Become aware of thesis statements in everyday life by paying attention to people’s opinions and their reasons for those opinions. Pay attention to your own everyday thesis statements as well, as these can become material for future essays.
Now that you have read about the contents of a good thesis statement and have seen examples, take a look at the pitfalls to avoid when composing your own thesis:
-
A thesis is weak when it is simply a declaration of your subject or a description of what you will discuss in your essay.
Weak thesis statement: My paper will explain why imagination is more important than knowledge.
-
A thesis is weak when it makes an unreasonable or outrageous claim or insults the opposing side.
Weak thesis statement: Religious radicals across America are trying to legislate their Puritanical beliefs by banning required high school books.
-
A thesis is weak when it contains an obvious fact or something that no one can disagree with or provides a dead end.
Weak thesis statement: Advertising companies use sex to sell their products.
-
A thesis is weak when the statement is too broad.
Weak thesis statement: The life of Abraham Lincoln was long and challenging.
Exercise 2
Read the following thesis statements. On a separate piece of paper, identify each as weak or strong. For those that are weak, list the reasons why. Then revise the weak statements so that they conform to the requirements of a strong thesis.
- The subject of this paper is my experience with ferrets as pets.
- The government must expand its funding for research on renewable energy resources in order to prepare for the impending end of oil.
- Edgar Allan Poe was a poet who lived in Baltimore during the nineteenth century.
- In this essay, I will give you lots of reasons why slot machines should not be legalized in Baltimore.
- Despite his promises during his campaign, President Kennedy took few executive measures to support civil rights legislation.
- Because many children’s toys have potential safety hazards that could lead to injury, it is clear that not all children’s toys are safe.
- My experience with young children has taught me that I want to be a disciplinary parent because I believe that a child without discipline can be a parent’s worst nightmare.
Writing at Work
Often in your career, you will need to ask your boss for something through an e-mail. Just as a thesis statement organizes an essay, it can also organize your e-mail request. While your e-mail will be shorter than an essay, using a thesis statement in your first paragraph quickly lets your boss know what you are asking for, why it is necessary, and what the benefits are. In short body paragraphs, you can provide the essential information needed to expand upon your request.
Thesis Statement Revision
Your thesis will probably change as you write, so you will need to modify it to reflect exactly what you have discussed in your essay. Remember from Chapter 7 "The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?" that your thesis statement begins as a working thesis statementAn indefinite statement that you make about your topic early in the writing process for the purpose of planning and guiding your writing., an indefinite statement that you make about your topic early in the writing process for the purpose of planning and guiding your writing.
Working thesis statements often become stronger as you gather information and form new opinions and reasons for those opinions. Revision helps you strengthen your thesis so that it matches what you have expressed in the body of the paper.
Tip
The best way to revise your thesis statement is to ask questions about it and then examine the answers to those questions. By challenging your own ideas and forming definite reasons for those ideas, you grow closer to a more precise point of view, which you can then incorporate into your thesis statement.
Ways to Revise Your Thesis
You can cut down on irrelevant aspects and revise your thesis by taking the following steps:
-
Pinpoint and replace all nonspecific words, such as people, everything, society, or life, with more precise words in order to reduce any vagueness.
Working thesis: Young people have to work hard to succeed in life.
Revised thesis: Recent college graduates must have discipline and persistence in order to find and maintain a stable job in which they can use and be appreciated for their talents.
The revised thesis makes a more specific statement about success and what it means to work hard. The original includes too broad a range of people and does not define exactly what success entails. By replacing those general words like people and work hard, the writer can better focus his or her research and gain more direction in his or her writing.
-
Clarify ideas that need explanation by asking yourself questions that narrow your thesis.
Working thesis: The welfare system is a joke.
Revised thesis: The welfare system keeps a socioeconomic class from gaining employment by alluring members of that class with unearned income, instead of programs to improve their education and skill sets.
A joke means many things to many people. Readers bring all sorts of backgrounds and perspectives to the reading process and would need clarification for a word so vague. This expression may also be too informal for the selected audience. By asking questions, the writer can devise a more precise and appropriate explanation for joke. The writer should ask himself or herself questions similar to the 5WH questions. (See Chapter 7 "The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?" for more information on the 5WH questions.) By incorporating the answers to these questions into a thesis statement, the writer more accurately defines his or her stance, which will better guide the writing of the essay.
-
Replace any linking verbsA verb that connects or links the subject of a sentence to a noun or adjective. with action verbs. Linking verbs are forms of the verb to be, a verb that simply states that a situation exists.
Working thesis: Kansas City schoolteachers are not paid enough.
Revised thesis: The Kansas City legislature cannot afford to pay its educators, resulting in job cuts and resignations in a district that sorely needs highly qualified and dedicated teachers.
The linking verb in this working thesis statement is the word are. Linking verbs often make thesis statements weak because they do not express action. Rather, they connect words and phrases to the second half of the sentence. Readers might wonder, “Why are they not paid enough?” But this statement does not compel them to ask many more questions. The writer should ask himself or herself questions in order to replace the linking verb with an action verb, thus forming a stronger thesis statement, one that takes a more definitive stance on the issue:
- Who is not paying the teachers enough?
- What is considered “enough”?
- What is the problem?
- What are the results
-
Omit any general claims that are hard to support.
Working thesis: Today’s teenage girls are too sexualized.
Revised thesis: Teenage girls who are captivated by the sexual images on MTV are conditioned to believe that a woman’s worth depends on her sensuality, a feeling that harms their self-esteem and behavior.
It is true that some young women in today’s society are more sexualized than in the past, but that is not true for all girls. Many girls have strict parents, dress appropriately, and do not engage in sexual activity while in middle school and high school. The writer of this thesis should ask the following questions:
- Which teenage girls?
- What constitutes “too” sexualized?
- Why are they behaving that way?
- Where does this behavior show up?
- What are the repercussions?
Exercise 3
In the first section of Chapter 7 "The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?", you determined your purpose for writing and your audience. You then completed a freewriting exercise about an event you recently experienced and chose a general topic to write about. Using that general topic, you then narrowed it down by answering the 5WH questions. After you answered these questions, you chose one of the three methods of prewriting and gathered possible supporting points for your working thesis statement.
Now, on a separate sheet of paper, write down your working thesis statement. Identify any weaknesses in this sentence and revise the statement to reflect the elements of a strong thesis statement. Make sure it is specific, precise, arguable, demonstrable, forceful, and confident.
Collaboration
Please share with a classmate and compare your answers.
Writing at Work
In your career you may have to write a project proposal that focuses on a particular problem in your company, such as reinforcing the tardiness policy. The proposal would aim to fix the problem; using a thesis statement would clearly state the boundaries of the problem and tell the goals of the project. After writing the proposal, you may find that the thesis needs revision to reflect exactly what is expressed in the body. Using the techniques from this chapter would apply to revising that thesis.
Key Takeaways
- Proper essays require a thesis statement to provide a specific focus and suggest how the essay will be organized.
- A thesis statement is your interpretation of the subject, not the topic itself.
- A strong thesis is specific, precise, forceful, confident, and is able to be demonstrated.
- A strong thesis challenges readers with a point of view that can be debated and can be supported with evidence.
- A weak thesis is simply a declaration of your topic or contains an obvious fact that cannot be argued.
- Depending on your topic, it may or may not be appropriate to use first person point of view.
- Revise your thesis by ensuring all words are specific, all ideas are exact, and all verbs express action.
8.2 Writing Body Paragraphs
Learning Objectives
- Select primary support related to your thesis.
- Support your topic sentences.
If your thesis gives the reader a roadmap to your essay, then body paragraphs should closely follow that map. The reader should be able to predict what follows your introductory paragraph by simply reading the thesis statement.
The body paragraphs present the evidence you have gathered to confirm your thesis. Before you begin to support your thesis in the body, you must find information from a variety of sources that support and give credit to what you are trying to prove.
Select Primary Support for Your Thesis
Without primary support, your argument is not likely to be convincing. Primary supportThe main points you use to support your thesis. can be described as the major points you choose to expand on your thesis. It is the most important information you select to argue for your point of view. Each point you choose will be incorporated into the topic sentence for each body paragraph you write. Your primary supporting points are further supported by supporting details within the paragraphs.
Tip
Remember that a worthy argument is backed by examples. In order to construct a valid argument, good writers conduct lots of background research and take careful notes. They also talk to people knowledgeable about a topic in order to understand its implications before writing about it.
Identify the Characteristics of Good Primary Support
In order to fulfill the requirements of good primary support, the information you choose must meet the following standards:
- Be specific. The main points you make about your thesis and the examples you use to expand on those points need to be specific. Use specific examples to provide the evidence and to build upon your general ideas. These types of examples give your reader something narrow to focus on, and if used properly, they leave little doubt about your claim. General examples, while they convey the necessary information, are not nearly as compelling or useful in writing because they are too obvious and typical.
- Be relevant to the thesis. Primary support is considered strong when it relates directly to the thesis. Primary support should show, explain, or prove your main argument without delving into irrelevant details. When faced with lots of information that could be used to prove your thesis, you may think you need to include it all in your body paragraphs. But effective writers resist the temptation to lose focus. Choose your examples wisely by making sure they directly connect to your thesis.
- Be detailed. Remember that your thesis, while specific, should not be very detailed. The body paragraphs are where you develop the discussion that a thorough essay requires. Using detailed support shows readers that you have considered all the facts and chosen only the most precise details to enhance your point of view.
Prewrite to Identify Primary Supporting Points for a Thesis Statement
Recall that when you prewrite you essentially make a list of examples or reasons why you support your stance. Stemming from each point, you further provide details to support those reasons. After prewriting, you are then able to look back at the information and choose the most compelling pieces you will use in your body paragraphs.
Exercise 1
Choose one of the following working thesis statements. On a separate sheet of paper, write for at least five minutes using one of the prewriting techniques you learned in Chapter 7 "The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?".
- Unleashed dogs on city streets are a dangerous nuisance.
- Students cheat for many different reasons.
- Drug use among teens and young adults is a problem.
- The most important change that should occur at my college or university is ____________________________________________.
Select the Most Effective Primary Supporting Points for a Thesis Statement
After you have prewritten about your working thesis statement, you may have generated a lot of information, which may be edited out later. Remember that your primary support must be relevant to your thesis. Remind yourself of your main argument, and delete any ideas that do not directly relate to it. Omitting unrelated ideas ensures that you will use only the most convincing information in your body paragraphs. Choose at least three of only the most compelling points. These will serve as the topic sentences for your body paragraphs.
Exercise 2
Refer to the previous exercise and select three of your most compelling reasons to support the thesis statement. Remember that the points you choose must be specific and relevant to the thesis. The statements you choose will be your primary support points, and you will later incorporate them into the topic sentences for the body paragraphs.
Collaboration
Please share with a classmate and compare your answers.
When you support your thesis, you are revealing evidence. Evidence includes anything that can help support your stance. The following are the kinds of evidence you will encounter as you conduct your research:
- Facts. Facts are the best kind of evidence to use because they often cannot be disputed. They can support your stance by providing background information on or a solid foundation for your point of view. However, some facts may still need explanation. For example, the sentence “The most populated state in the United States is California” is a pure fact, but it may require some explanation to make it relevant to your specific argument.
- Judgments.JudgmentsA conclusion that is inferred from the facts of a matter. are conclusions drawn from the given facts. Judgments are more credible than opinions because they are founded upon careful reasoning and examination of a topic.
- Testimony.TestimonyQuotations from people involved in a matter. It lends authenticity and credibility to an argument. consists of direct quotations from either an eyewitness or an expert witness. An eyewitness is someone who has direct experience with a subject; he adds authenticity to an argument based on facts. An expert witness is a person who has extensive experience with a topic. This person studies the facts and provides commentary based on either facts or judgments, or both. An expert witness adds authority and credibility to an argument.
- Personal observation. Personal observation is similar to testimony, but personal observation consists of your testimony. It reflects what you know to be true because you have experiences and have formed either opinions or judgments about them. For instance, if you are one of five children and your thesis states that being part of a large family is beneficial to a child’s social development, you could use your own experience to support your thesis.
Writing at Work
In any job where you devise a plan, you will need to support the steps that you lay out. This is an area in which you would incorporate primary support into your writing. Choosing only the most specific and relevant information to expand upon the steps will ensure that your plan appears well-thought-out and precise.
Tip
You can consult a vast pool of resources to gather support for your stance. Citing relevant information from reliable sources ensures that your reader will take you seriously and consider your assertions. Use any of the following sources for your essay: newspapers or news organization websites, magazines, encyclopedias, and scholarly journals, which are periodicals that address topics in a specialized field.
Choose Supporting Topic Sentences
Each body paragraph contains a topic sentenceThe sentence in a paragraph that controls the point of the paragraph. It is most often located at the beginning of a paragraph and makes the structure of a text and the writer’s basic argument easy to locate and comprehend. that states one aspect of your thesis and then expands upon it. Like the thesis statement, each topic sentence should be specific and supported by concrete details, facts, or explanations.
Each body paragraph should comprise the following elements.
topic sentence + supporting details (examples, reasons, or arguments)
As you read in Chapter 7 "The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?", topic sentences indicate the location and main points of the basic arguments of your essay. These sentences are vital to writing your body paragraphs because they always refer back to and support your thesis statement. Topic sentences are linked to the ideas you have introduced in your thesis, thus reminding readers what your essay is about. A paragraph without a clearly identified topic sentence may be unclear and scattered, just like an essay without a thesis statement.
Tip
Unless your teacher instructs otherwise, you should include at least three body paragraphs in your essay. A five-paragraph essay, including the introduction and conclusion, is commonly the standard for exams and essay assignments.
Consider the following the thesis statement:

The following topic sentence is a primary support point for the thesis. The topic sentence states exactly what the controlling idea of the paragraph is. Later, you will see the writer immediately provide support for the sentence.

Exercise 3
In Note 8.19 "Exercise 2", you chose three of your most convincing points to support the thesis statement you selected from the list. Take each point and incorporate it into a topic sentence for each body paragraph.
Supporting point 1: ____________________________________________
Topic sentence: ____________________________________________
Supporting point 2: ____________________________________________
Topic sentence: ____________________________________________
Supporting point 3: ____________________________________________
Topic sentence: ____________________________________________
Collaboration
Please share with a classmate and compare your answers.
Draft Supporting Detail Sentences for Each Primary Support Sentence
After deciding which primary support points you will use as your topic sentences, you must add details to clarify and demonstrate each of those points. These supporting details provide examples, facts, or evidence that support the topic sentence.
The writer drafts possible supporting detail sentences for each primary support sentence based on the thesis statement:

The following paragraph contains supporting detail sentences for the primary support sentence (the topic sentence), which is underlined.

Exercise 4
Using the three topic sentences you composed for the thesis statement in Note 8.18 "Exercise 1", draft at least three supporting details for each point.
Thesis statement: ____________________________________________
Primary supporting point 1: ____________________________________________
Supporting details: ____________________________________________
Primary supporting point 2: ____________________________________________
Supporting details: ____________________________________________
Primary supporting point 3: ____________________________________________
Supporting details: ____________________________________________
Tip
You have the option of writing your topic sentences in one of three ways. You can state it at the beginning of the body paragraph, or at the end of the paragraph, or you do not have to write it at all. This is called an implied topic sentence. An implied topic sentence lets readers form the main idea for themselves. For beginning writers, it is best to not use implied topic sentences because it makes it harder to focus your writing. Your instructor may also want to clearly identify the sentences that support your thesis. For more information on the placement of thesis statements and implied topic statements, see Chapter 7 "The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?".
Tip
Print out the first draft of your essay and use a highlighter to mark your topic sentences in the body paragraphs. Make sure they are clearly stated and accurately present your paragraphs, as well as accurately reflect your thesis. If your topic sentence contains information that does not exist in the rest of the paragraph, rewrite it to more accurately match the rest of the paragraph.
Key Takeaways
- Your body paragraphs should closely follow the path set forth by your thesis statement.
- Strong body paragraphs contain evidence that supports your thesis.
- Primary support comprises the most important points you use to support your thesis.
- Strong primary support is specific, detailed, and relevant to the thesis.
- Prewriting helps you determine your most compelling primary support.
- Evidence includes facts, judgments, testimony, and personal observation.
- Reliable sources may include newspapers, magazines, academic journals, books, encyclopedias, and firsthand testimony.
- A topic sentence presents one point of your thesis statement while the information in the rest of the paragraph supports that point.
- A body paragraph comprises a topic sentence plus supporting details.
8.3 Organizing Your Writing
Learning Objectives
- Understand how and why organizational techniques help writers and readers stay focused.
- Assess how and when to use chronological order to organize an essay.
- Recognize how and when to use order of importance to organize an essay.
- Determine how and when to use spatial order to organize an essay.
The method of organization you choose for your essay is just as important as its content. Without a clear organizational pattern, your reader could become confused and lose interest. The way you structure your essay helps your readers draw connections between the body and the thesis, and the structure also keeps you focused as you plan and write the essay. Choosing your organizational pattern before you outline ensures that each body paragraph works to support and develop your thesis.
This section covers three ways to organize body paragraphs:
- Chronological order
- Order of importance
- Spatial order
When you begin to draft your essay, your ideas may seem to flow from your mind in a seemingly random manner. Your readers, who bring to the table different backgrounds, viewpoints, and ideas, need you to clearly organize these ideas in order to help process and accept them.
A solid organizational pattern gives your ideas a path that you can follow as you develop your draft. Knowing how you will organize your paragraphs allows you to better express and analyze your thoughts. Planning the structure of your essay before you choose supporting evidence helps you conduct more effective and targeted research.
Chronological Order
In Chapter 7 "The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?", you learned that chronological arrangement has the following purposes:
- To explain the history of an event or a topic
- To tell a story or relate an experience
- To explain how to do or to make something
- To explain the steps in a process
Chronological orderAn organizational method that arranges events or steps in the order that they have occurred or will occur. is mostly used in expository writingWriting that conveys facts or descriptions., which is a form of writing that narrates, describes, informs, or explains a process. When using chronological order, arrange the events in the order that they actually happened, or will happen if you are giving instructions. This method requires you to use words such as first, second, then, after that, later, and finally. These transition words guide you and your reader through the paper as you expand your thesis.
For example, if you are writing an essay about the history of the airline industry, you would begin with its conception and detail the essential timeline events up until present day. You would follow the chain of events using words such as first, then, next, and so on.
Writing at Work
At some point in your career you may have to file a complaint with your human resources department. Using chronological order is a useful tool in describing the events that led up to your filing the grievance. You would logically lay out the events in the order that they occurred using the key transition words. The more logical your complaint, the more likely you will be well received and helped.
Exercise 1
Choose an accomplishment you have achieved in your life. The important moment could be in sports, schooling, or extracurricular activities. On your own sheet of paper, list the steps you took to reach your goal. Try to be as specific as possible with the steps you took. Pay attention to using transition words to focus your writing.
Keep in mind that chronological order is most appropriate for the following purposes:
- Writing essays containing heavy research
- Writing essays with the aim of listing, explaining, or narrating
- Writing essays that analyze literary works such as poems, plays, or books
Tip
When using chronological order, your introduction should indicate the information you will cover and in what order, and the introduction should also establish the relevance of the information. Your body paragraphs should then provide clear divisions or steps in chronology. You can divide your paragraphs by time (such as decades, wars, or other historical events) or by the same structure of the work you are examining (such as a line-by-line explication of a poem).
Exercise 2
On a separate sheet of paper, write a paragraph that describes a process you are familiar with and can do well. Assume that your reader is unfamiliar with the procedure. Remember to use the chronological key words, such as first, second, then, and finally.
Order of Importance
Recall from Chapter 7 "The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?" that order of importanceA method of organization that arranges ideas according to their significance. is best used for the following purposes:
- Persuading and convincing
- Ranking items by their importance, benefit, or significance
- Illustrating a situation, problem, or solution
Most essays move from the least to the most important point, and the paragraphs are arranged in an effort to build the essay’s strength. Sometimes, however, it is necessary to begin with your most important supporting point, such as in an essay that contains a thesis that is highly debatable. When writing a persuasive essay, it is best to begin with the most important point because it immediately captivates your readers and compels them to continue reading.
For example, if you were supporting your thesis that homework is detrimental to the education of high school students, you would want to present your most convincing argument first, and then move on to the less important points for your case.
Some key transitional words you should use with this method of organization are most importantly, almost as importantly, just as importantly, and finally.
Writing at Work
During your career, you may be required to work on a team that devises a strategy for a specific goal of your company, such as increasing profits. When planning your strategy you should organize your steps in order of importance. This demonstrates the ability to prioritize and plan. Using the order of importance technique also shows that you can create a resolution with logical steps for accomplishing a common goal.
Exercise 3
On a separate sheet of paper, write a paragraph that discusses a passion of yours. Your passion could be music, a particular sport, filmmaking, and so on. Your paragraph should be built upon the reasons why you feel so strongly. Briefly discuss your reasons in the order of least to greatest importance.
Spatial Order
As stated in Chapter 7 "The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?", spatial orderA method of organization that arranges ideas according to physical characteristics or appearance. is best used for the following purposes:
- Helping readers visualize something as you want them to see it
- Evoking a scene using the senses (sight, touch, taste, smell, and sound)
- Writing a descriptive essay
Spatial order means that you explain or describe objects as they are arranged around you in your space, for example in a bedroom. As the writer, you create a picture for your reader, and their perspective is the viewpoint from which you describe what is around you.
The view must move in an orderly, logical progression, giving the reader clear directional signals to follow from place to place. The key to using this method is to choose a specific starting point and then guide the reader to follow your eye as it moves in an orderly trajectory from your starting point.
Pay attention to the following student’s description of her bedroom and how she guides the reader through the viewing process, foot by foot.

The paragraph incorporates two objectives you have learned in this chapter: using an implied topic sentence and applying spatial order. Often in a descriptive essay, the two work together.
The following are possible transition words to include when using spatial order:
- Just to the left or just to the right
- Behind
- Between
- On the left or on the right
- Across from
- A little further down
- To the south, to the east, and so on
- A few yards away
- Turning left or turning right
Exercise 4
On a separate sheet of paper, write a paragraph using spatial order that describes your commute to work, school, or another location you visit often.
Collaboration
Please share with a classmate and compare your answers.
Key Takeaways
- The way you organize your body paragraphs ensures you and your readers stay focused on and draw connections to, your thesis statement.
- A strong organizational pattern allows you to articulate, analyze, and clarify your thoughts.
- Planning the organizational structure for your essay before you begin to search for supporting evidence helps you conduct more effective and directed research.
- Chronological order is most commonly used in expository writing. It is useful for explaining the history of your subject, for telling a story, or for explaining a process.
- Order of importance is most appropriate in a persuasion paper as well as for essays in which you rank things, people, or events by their significance.
- Spatial order describes things as they are arranged in space and is best for helping readers visualize something as you want them to see it; it creates a dominant impression.
8.4 Writing Introductory and Concluding Paragraphs
Learning Objectives
- Recognize the importance of strong introductory and concluding paragraphs.
- Learn to engage the reader immediately with the introductory paragraph.
- Practice concluding your essays in a more memorable way.
Picture your introduction as a storefront window: You have a certain amount of space to attract your customers (readers) to your goods (subject) and bring them inside your store (discussion). Once you have enticed them with something intriguing, you then point them in a specific direction and try to make the sale (convince them to accept your thesis).
Your introduction is an invitation to your readers to consider what you have to say and then to follow your train of thought as you expand upon your thesis statement.
An introduction serves the following purposes:
- Establishes your voice and tone, or your attitude, toward the subject
- Introduces the general topic of the essay
- States the thesis that will be supported in the body paragraphs
First impressions are crucial and can leave lasting effects in your reader’s mind, which is why the introduction is so important to your essay. If your introductory paragraph is dull or disjointed, your reader probably will not have much interest in continuing with the essay.
Attracting Interest in Your Introductory Paragraph
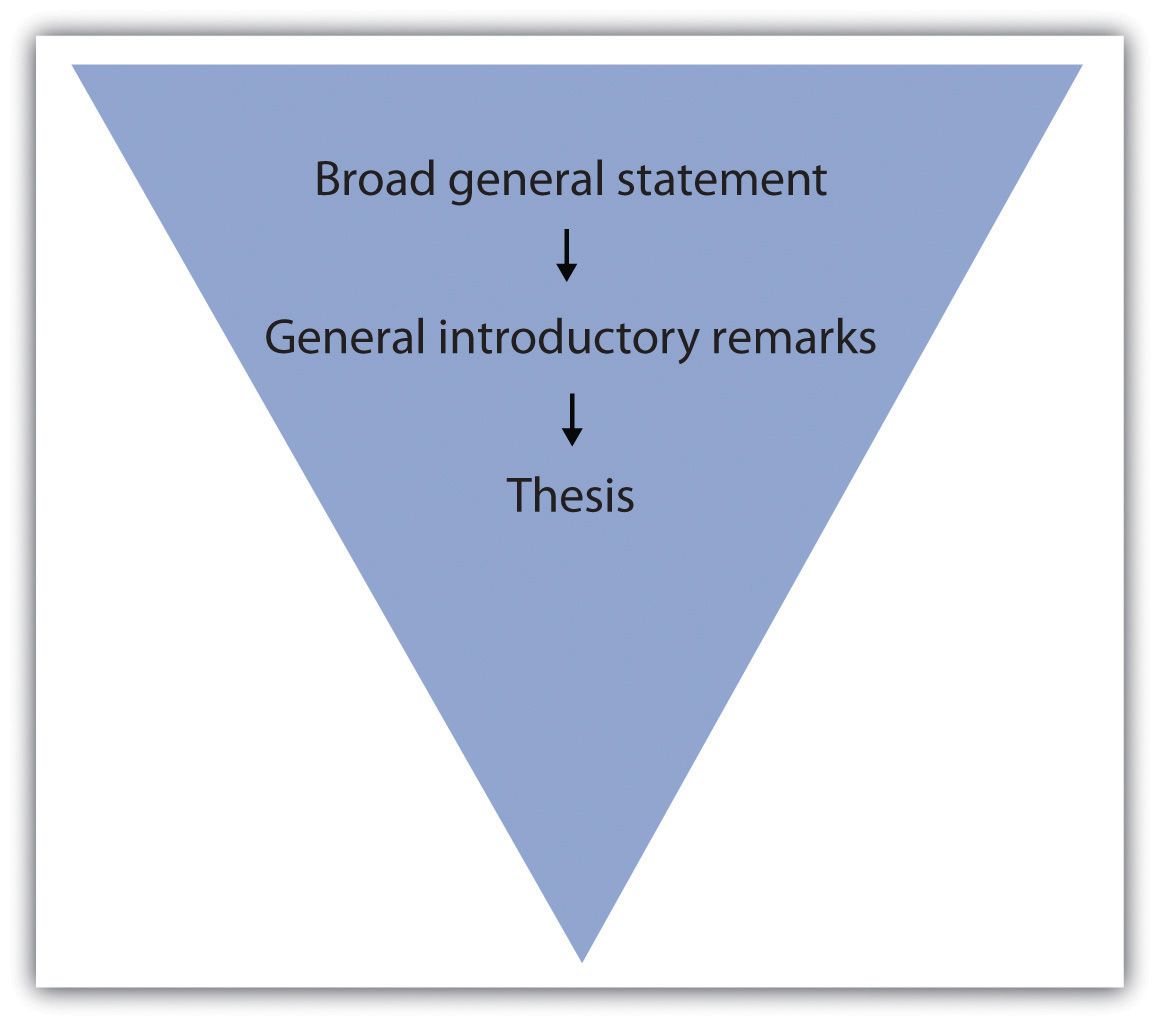
Your introduction should begin with an engaging statement devised to provoke your readers’ interest. In the next few sentences, introduce them to your topic by stating general facts or ideas about the subject. As you move deeper into your introduction, you gradually narrow the focus, moving closer to your thesis. Moving smoothly and logically from your introductory remarks to your thesis statement can be achieved using a funnel techniqueA writing device that begins with a broad statement and then gradually moves toward the heart of the matter., as illustrated in the diagram in Figure 8.1 "Funnel Technique".
Figure 8.1 Funnel Technique
Exercise 1
On a separate sheet of paper, jot down a few general remarks that you can make about the topic for which you formed a thesis in Section 8.1 "Developing a Strong, Clear Thesis Statement".
Immediately capturing your readers’ interest increases the chances of having them read what you are about to discuss. You can garner curiosity for your essay in a number of ways. Try to get your readers personally involved by doing any of the following:
- Appealing to their emotions
- Using logic
- Beginning with a provocative question or opinion
- Opening with a startling statistic or surprising fact
- Raising a question or series of questions
- Presenting an explanation or rationalization for your essay
- Opening with a relevant quotation or incident
- Opening with a striking image
- Including a personal anecdote
Tip
Remember that your diction, or word choice, while always important, is most crucial in your introductory paragraph. Boring diction could extinguish any desire a person might have to read through your discussion. Choose words that create images or express action. For more information on diction, see Chapter 3 "Working with Words: Which Word Is Right?".
In Chapter 7 "The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?", you followed Mariah as she moved through the writing process. In this chapter, Mariah writes her introduction and conclusion for the same essay. Mariah incorporates some of the introductory elements into her introductory paragraph, which she previously outlined in Chapter 7 "The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?". Her thesis statement is underlined.

Tip
If you have trouble coming up with a provocative statement for your opening, it is a good idea to use a relevant, attention-grabbing quote about your topic. Use a search engine to find statements made by historical or significant figures about your subject.
Writing at Work
In your job field, you may be required to write a speech for an event, such as an awards banquet or a dedication ceremony. The introduction of a speech is similar to an essay because you have a limited amount of space to attract your audience’s attention. Using the same techniques, such as a provocative quote or an interesting statistic, is an effective way to engage your listeners. Using the funnel approach also introduces your audience to your topic and then presents your main idea in a logical manner.
Exercise 2
Reread each sentence in Mariah’s introductory paragraph. Indicate which techniques she used and comment on how each sentence is designed to attract her readers’ interest.
Writing a Conclusion
It is not unusual to want to rush when you approach your conclusion, and even experienced writers may fade. But what good writers remember is that it is vital to put just as much attention into the conclusion as in the rest of the essay. After all, a hasty ending can undermine an otherwise strong essay.
A conclusion that does not correspond to the rest of your essay, has loose ends, or is unorganized can unsettle your readers and raise doubts about the entire essay. However, if you have worked hard to write the introduction and body, your conclusion can often be the most logical part to compose.
The Anatomy of a Strong Conclusion
Keep in mind that the ideas in your conclusion must conform to the rest of your essay. In order to tie these components together, restate your thesis at the beginning of your conclusion. This helps you assemble, in an orderly fashion, all the information you have explained in the body. Repeating your thesis reminds your readers of the major arguments you have been trying to prove and also indicates that your essay is drawing to a close. A strong conclusion also reviews your main points and emphasizes the importance of the topic.
The construction of the conclusion is similar to the introduction, in which you make general introductory statements and then present your thesis. The difference is that in the conclusion you first paraphraseTo restate ideas or information from sources using one’s own words and sentence structures., or state in different words, your thesis and then follow up with general concluding remarks. These sentences should progressively broaden the focus of your thesis and maneuver your readers out of the essay.
Many writers like to end their essays with a final emphatic statement. This strong closing statement will cause your readers to continue thinking about the implications of your essay; it will make your conclusion, and thus your essay, more memorable. Another powerful technique is to challenge your readers to make a change in either their thoughts or their actions. Challenging your readers to see the subject through new eyes is a powerful way to ease yourself and your readers out of the essay.
Tip
When closing your essay, do not expressly state that you are drawing to a close. Relying on statements such as in conclusion, it is clear that, as you can see, or in summation is unnecessary and can be considered trite.
Tip
It is wise to avoid doing any of the following in your conclusion:
- Introducing new material
- Contradicting your thesis
- Changing your thesis
- Using apologies or disclaimers
Introducing new material in your conclusion has an unsettling effect on your reader. When you raise new points, you make your reader want more information, which you could not possibly provide in the limited space of your final paragraph.
Contradicting or changing your thesis statement causes your readers to think that you do not actually have a conviction about your topic. After all, you have spent several paragraphs adhering to a singular point of view. When you change sides or open up your point of view in the conclusion, your reader becomes less inclined to believe your original argument.
By apologizing for your opinion or stating that you know it is tough to digest, you are in fact admitting that even you know what you have discussed is irrelevant or unconvincing. You do not want your readers to feel this way. Effective writers stand by their thesis statement and do not stray from it.
Exercise 3
On a separate sheet of a paper, restate your thesis from Note 8.52 "Exercise 2" of this section and then make some general concluding remarks. Next, compose a final emphatic statement. Finally, incorporate what you have written into a strong conclusion paragraph for your essay.
Collaboration
Please share with a classmate and compare your answers
Mariah incorporates some of these pointers into her conclusion. She has paraphrased her thesis statement in the first sentence.

Tip
Make sure your essay is balanced by not having an excessively long or short introduction or conclusion. Check that they match each other in length as closely as possible, and try to mirror the formula you used in each. Parallelism strengthens the message of your essay.
Writing at Work
On the job you will sometimes give oral presentations based on research you have conducted. A concluding statement to an oral report contains the same elements as a written conclusion. You should wrap up your presentation by restating the purpose of the presentation, reviewing its main points, and emphasizing the importance of the material you presented. A strong conclusion will leave a lasting impression on your audience.
Key Takeaways
- A strong opening captures your readers’ interest and introduces them to your topic before you present your thesis statement.
- An introduction should restate your thesis, review your main points, and emphasize the importance of the topic.
- The funnel technique to writing the introduction begins with generalities and gradually narrows your focus until you present your thesis.
- A good introduction engages people’s emotions or logic, questions or explains the subject, or provides a striking image or quotation.
- Carefully chosen diction in both the introduction and conclusion prevents any confusing or boring ideas.
- A conclusion that does not connect to the rest of the essay can diminish the effect of your paper.
- The conclusion should remain true to your thesis statement. It is best to avoid changing your tone or your main idea and avoid introducing any new material.
- Closing with a final emphatic statement provides closure for your readers and makes your essay more memorable.
8.5 Writing Essays: End-of-Chapter Exercises
Exercises
- On a separate sheet of paper, choose one of the examples of a proper thesis statement from this chapter (one that interests you) and form three supporting points for that statement. After you have formed your three points, write a topic sentence for each body paragraph. Make sure that your topic sentences can be backed up with examples and details.
- Group activity. Choose one of the topics from Note 8.5 "Exercise 1" in Section 8.1 "Developing a Strong, Clear Thesis Statement" and form a yes-or-no question about that topic. Then, take a survey of the people in your class to find out how they feel about the subject. Using the majority vote, ask those people to write on slips of paper the reasons for their opinion. Using the data you collect, form a thesis statement based on your classmates’ perspectives on the topic and their reasons.
- On a separate sheet of a paper, write an introduction for an essay based on the thesis statement from the group activity using the techniques for introductory paragraphs that you learned in this chapter.
- Start a journal in which you record “spoken” thesis statements. Start listening closely to the opinions expressed by your teachers, classmates, friends, and family members. Ask them to provide at least three reasons for their opinion and record them in the journal. Use this as material for future essays.
- Open a magazine and read a lengthy article. See if you can pinpoint the thesis statement as well as the topic sentence for each paragraph and its supporting details.




