This is “Conclusion”, section 9.5 from the book Strategic Management: Evaluation and Execution (v. 1.0). For details on it (including licensing), click here.
For more information on the source of this book, or why it is available for free, please see the project's home page. You can browse or download additional books there. To download a .zip file containing this book to use offline, simply click here.
9.5 Conclusion
This chapter explains elements of organizational design that are vital for executing strategy. Leaders of firms, ranging from the smallest sole proprietorship to the largest global corporation, must make decisions about the delegation of authority and responsibility when organizing activities within their firms. Deciding how to best divide labor to increase efficiency and effectiveness is often the starting point for more complex decisions that lead to the creation of formal organizational charts. While small businesses rarely create organization charts, firms that embrace functional, multidivisional, and matrix structures often have reporting relationships with considerable complexity. To execute strategy effectively, managers also depend on the skillful use of organizational control systems that involve output, behavioral, and clan controls. Although introducing more efficient business practices to improve organizational functioning is desirable, executives need to avoid letting their firms become “out of control” by being skeptical of management fads. Finally, the legal form a business takes is an important decision with implications for a firm’s organizational structure.
Exercises
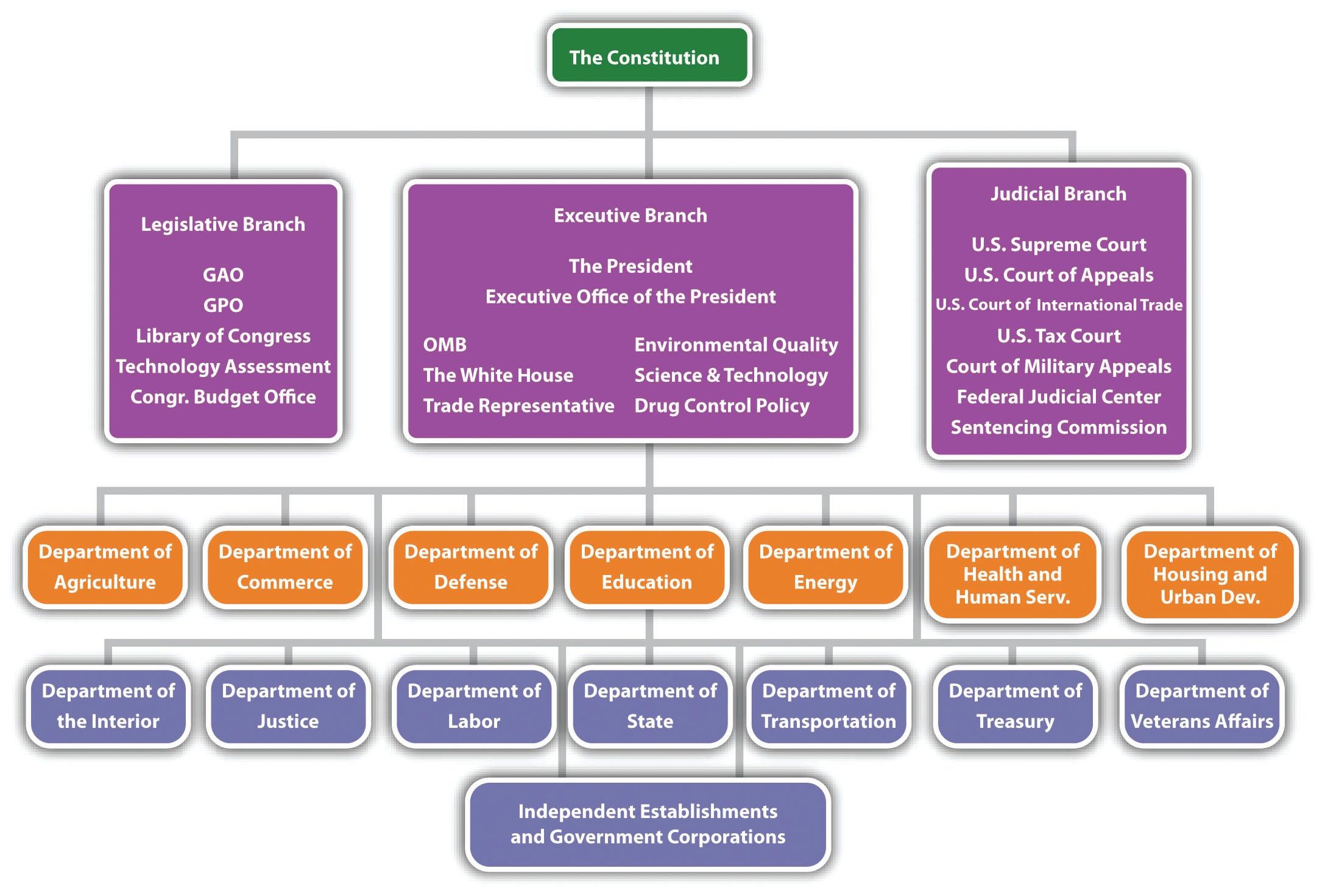
- The following chart is an organizational chart for the US federal government. What type of the four structures mentioned in this chapter best fits what you see in this chart?
- How does this structure explain why the government seems to move at an incredibly slow pace?
- What changes could be made to speed up the government? Would they be beneficial?




