This is “Effect of a Real GDP Increase (Economic Growth) on Interest Rates”, section 18.11 from the book Policy and Theory of International Economics (v. 1.0). For details on it (including licensing), click here.
For more information on the source of this book, or why it is available for free, please see the project's home page. You can browse or download additional books there. To download a .zip file containing this book to use offline, simply click here.
18.11 Effect of a Real GDP Increase (Economic Growth) on Interest Rates
Learning Objective
- Learn how a change in real GDP affects the equilibrium interest rate.
Finally, let’s consider the effects of an increase in real gross domestic product (GDP). Such an increase represents economic growth. Thus the study of the effects of a real GDP increase is the same as asking how economic growth will affect interest rates.
GDP may increase for a variety of reasons, which are discussed in subsequent chapters. For now, we will imagine that GDP increases for some unspecified reason and consider the consequences of such a change in the money market.
Suppose the money market is originally in equilibrium at point A in Figure 18.5 "Effects of an Increase in Real GDP" with real money supply MS/P$ and interest rate i$′. Suppose real GDP (Y$) increases, ceteris paribus. Again, the ceteris paribus assumption means that we assume all other exogenous variables in the model remain fixed at their original levels. In this exercise, it means that the money supply (MS) and the price level (P$) remain fixed. An increase in GDP will raise the demand for money because people will need more money to make the transactions necessary to purchase the new GDP. In other words, real money demand rises due to the transactions demand effect. This increase is reflected in the rightward shift of the real money demand function from L(i$, Y$′) to L(i$, Y$″).
Figure 18.5 Effects of an Increase in Real GDP
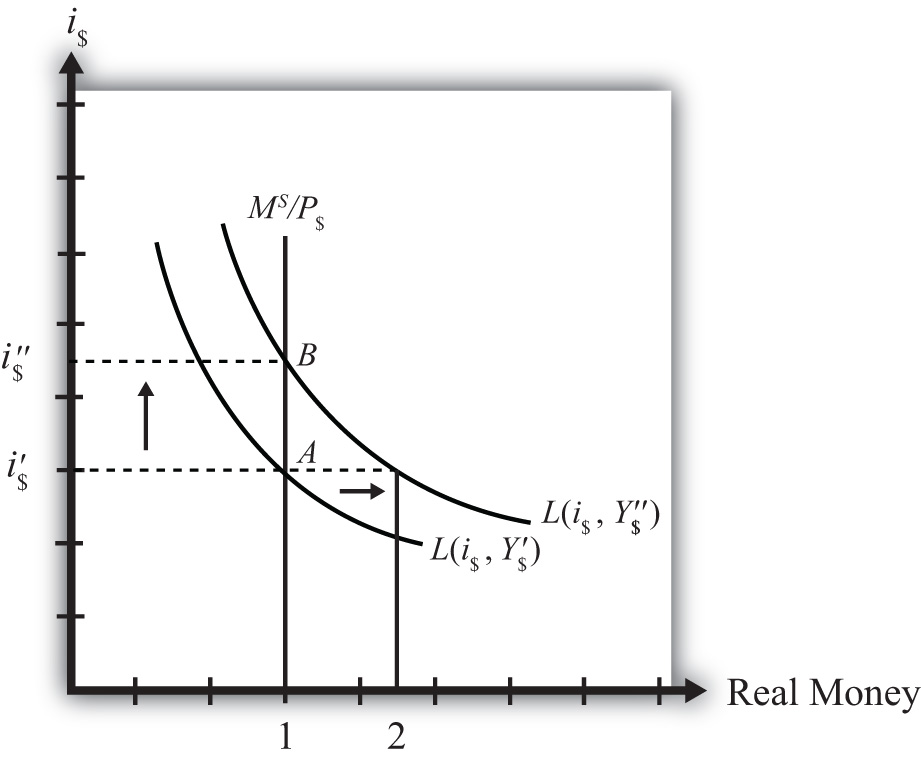
At the original interest rate, i$′, real money demand has increased to level 2 along the horizontal axis while real money supply remains at level 1. This means that real money demand exceeds real money supply and the current interest rate is lower than the equilibrium rate. Adjustment to the higher interest rate will follow the “interest rate too low” equilibrium story.
The final equilibrium will occur at point B on the diagram. As the interest rate rises from i$′ to i$″, real money demand will have fallen from level 2 to level 1. Thus an increase in real GDP (i.e., economic growth) will cause an increase in average interest rates in an economy. In contrast, a decrease in real GDP (a recession) will cause a decrease in average interest rates in an economy.
Key Takeaway
- An increase in real gross domestic product (i.e., economic growth), ceteris paribus, will cause an increase in average interest rates in an economy. In contrast, a decrease in real GDP (a recession), ceteris paribus, will cause a decrease in average interest rates in an economy.
Exercise
-
Jeopardy Questions. As in the popular television game show, you are given an answer to a question and you must respond with the question. For example, if the answer is “a tax on imports,” then the correct question is “What is a tariff?”
- The term used to describe a percentage increase in real GDP over a period of time.
- Of increase, decrease, or stay the same, the effect on the equilibrium interest rate when real GDP decreases, ceteris paribus.
- Of increase, decrease, or stay the same, the effect on the equilibrium interest rate when real GDP increases, ceteris paribus.




