This is “The Economic Effects of Protection: An Example”, section 10.3 from the book Policy and Theory of International Economics (v. 1.0). For details on it (including licensing), click here.
For more information on the source of this book, or why it is available for free, please see the project's home page. You can browse or download additional books there. To download a .zip file containing this book to use offline, simply click here.
10.3 The Economic Effects of Protection: An Example
Learning Objective
- Depict numerical values for the welfare effects of a tariff by a small country.
Consider the market for blue jeans in a small importing country, depicted in Figure 10.1 "A Market for Blue Jeans". Suppose a sudden increase in the world supply of jeans causes the world market price to fall from $35 to $30. The price decrease causes an increase in domestic demand from nine to ten million pairs of jeans, a decrease in domestic supply from eight to six million pairs, and an increase in imports from one to four million.
Figure 10.1 A Market for Blue Jeans
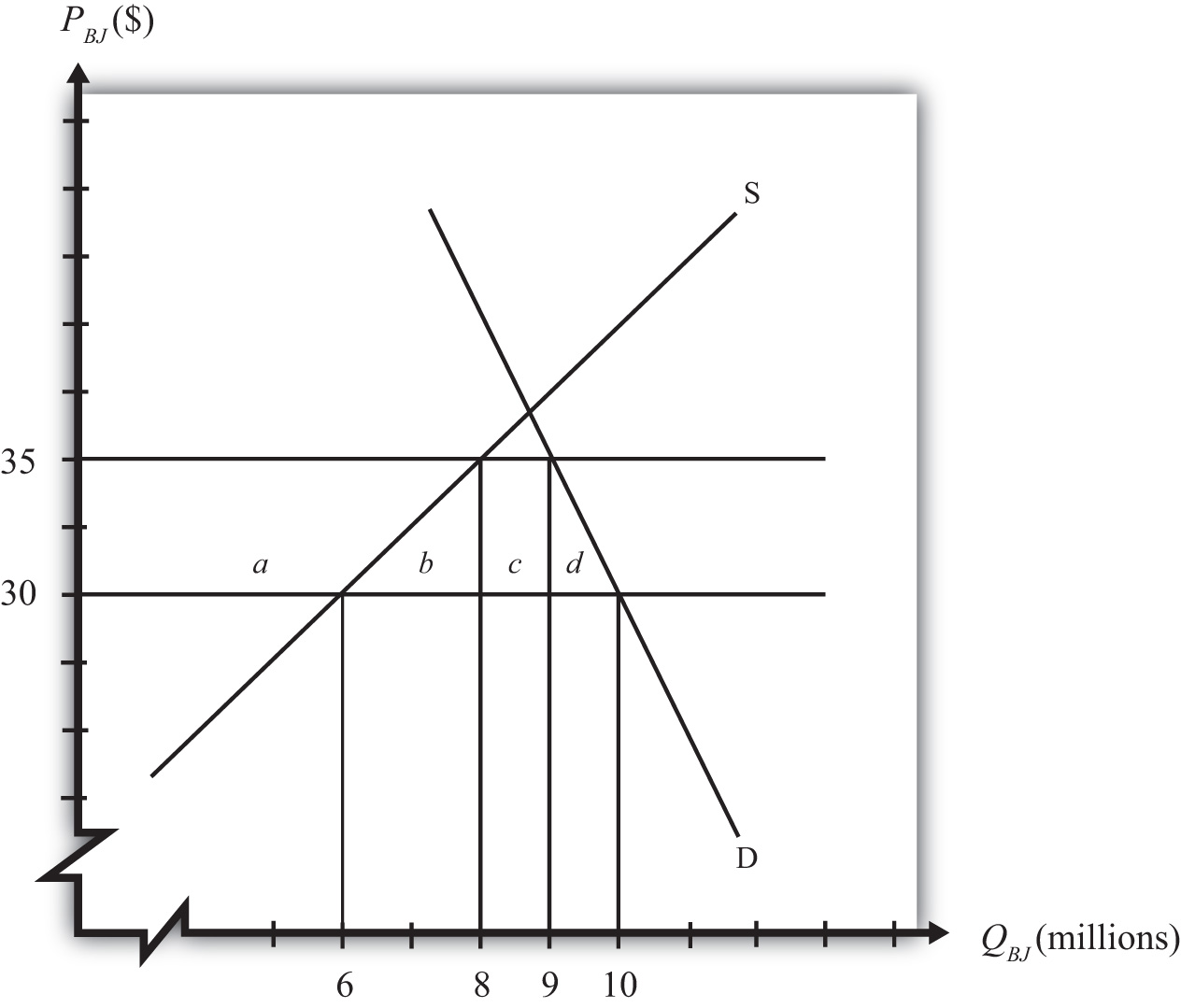
Because of these market changes, suppose that the import-competing industry uses its trade union to organize a petition to the government for temporary protection. Let’s imagine that the industry calls for a $5 tariff so as to reverse the effects of the import surge. Note that this type of action is allowable to World Trade Organization (WTO) member countries under the “escape clause” or “safeguards clause.”
We can use the measures of producer surplus and consumer surplus to calculate the effects of a $5 tariff. These effects are summarized in Table 10.1 "Welfare Effects of an Import Tariff". The dollar values are calculated from the respective areas on the graph in Figure 10.1 "A Market for Blue Jeans".
Table 10.1 Welfare Effects of an Import Tariff
| Area on Graph | $ Value | |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Surplus | − (a + b + c + d) | − $47.5 million |
| Producer Surplus | + a | + $35 million |
| Govt. Revenue | + c | + $5 million |
| National Welfare | − (b + d) | − $7.5 million |
Notice that consumers lose more than the gains that accrue to the domestic producers and the government combined. This is why national welfare is shown to decrease by $7.5 million.
In order to assess the political ramifications of this potential policy, we will make some additional assumptions. In most markets, the number of individuals that makes up the demand side of the market is much larger than the number of firms that makes up the domestic import-competing industry. Suppose, then, that the consumers in this market are made up of millions of individual households, each of which purchases, at most, one pair of jeans. Suppose the domestic blue jeans industry is made up of thirty-five separate firms.
Key Takeaway
- With quantities, prices, and the tariff rate specified, actual values for the changes in consumer and producer surplus and government revenue can be determined.
Exercise
-
Suppose the supply and demand curves for bottles of Coke are given by,
S = 10P – 7 D = 13 – 5Pwhere P is the price of Coke per bottle, D is the quantity of Coke demand (in millions of bottles), and S is the quantity of Coke supply (in millions of bottles). Suppose the free trade price of Coke is $1.00 and that a tariff of $0.20 is being considered by the government. If the country is a small importer calculate the following:
- The value of the increase in producer surplus expected due to the tariff.
- The value of the decrease in consumer surplus expected due to the tariff.
- The value of the tariff revenue expected due to the tariff.
- The value of the change in national welfare expected due to the tariff.




