This is “Voluntary Export Restraints: Large Country Welfare Effects”, section 7.21 from the book Policy and Theory of International Economics (v. 1.0). For details on it (including licensing), click here.
For more information on the source of this book, or why it is available for free, please see the project's home page. You can browse or download additional books there. To download a .zip file containing this book to use offline, simply click here.
7.21 Voluntary Export Restraints: Large Country Welfare Effects
Learning Objectives
- Use a partial equilibrium diagram to identify the welfare effects of a voluntary export restraint (VER) on producer and consumer groups and the government in the exporting and importing countries.
- Calculate the national and world welfare effects of a VER in the case of a large country.
Suppose for simplicity that there are only two trading countries: one importing country and one exporting country. The supply and demand curves for the two countries are shown in Figure 7.36 "Welfare Effects of a VER: Large Country Case". PFT is the free trade equilibrium price. At that price, the excess demand by the importing country equals excess supply by the exporter.
Figure 7.36 Welfare Effects of a VER: Large Country Case
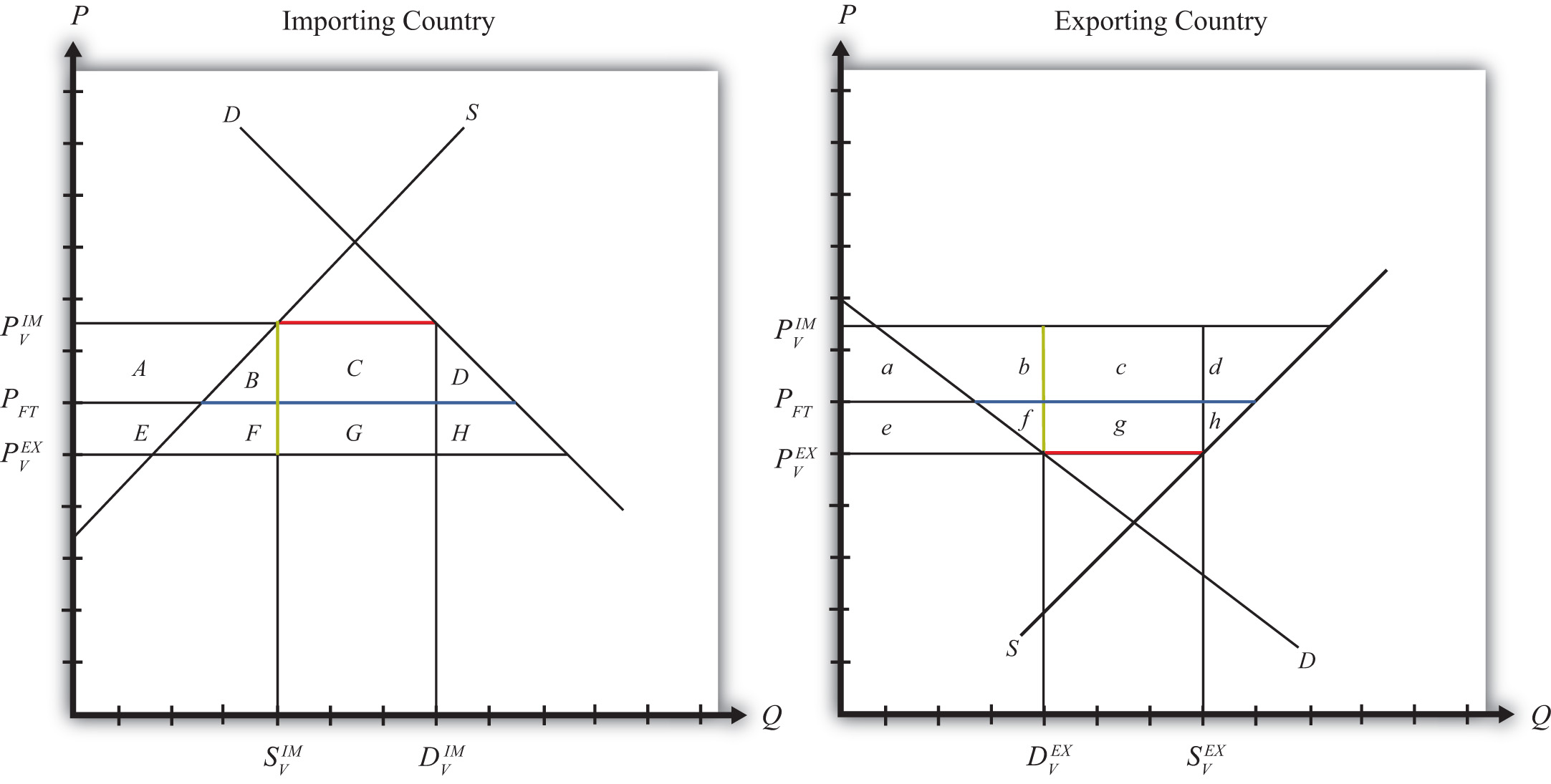
The quantity of imports and exports is shown as the blue line segment on each country’s graph (the horizontal distance between the supply and demand curves at the free trade price). Suppose the large exporting country implements a binding voluntary export restraint set equal to the length of the red line segment. When a new equilibrium is reached, the price in the importing country will rise to the level at which import demand is equal to the quota level. The price in the exporting country will fall until export supply is equal to the quota level.
Table 7.15 "Welfare Effects of a Voluntary Export Restraint" provides a summary of the direction and magnitude of the welfare effects to producers, consumers, and the governments in the importing and exporting countries. The aggregate national welfare effects and the world welfare effects are also shown.
Table 7.15 Welfare Effects of a Voluntary Export Restraint
| Importing Country | Exporting Country | |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer Surplus | − (A + B + C + D) | + e |
| Producer Surplus | + A | − (e + f + g + h) |
| Quota Rents | 0 | + (c + g) |
| National Welfare | − (B + C + D) | c − (f + h) |
| World Welfare | − (B + D) − (f + h) |
Refer to Table 7.15 "Welfare Effects of a Voluntary Export Restraint" and Figure 7.36 "Welfare Effects of a VER: Large Country Case" to see how the magnitudes of the changes are represented.
VER effects on the exporting country’s consumers. Consumers of the product in the exporting country experience an increase in well-being as a result of the VER. The decrease in their domestic price raises the amount of consumer surplus in the market.
VER effects on the exporting country’s producers. Producers in the exporting country experience a decrease in well-being as a result of the quota. The decrease in the price of their product in their own market decreases producer surplus in the industry. The price decline also induces a decrease in output, a decrease in employment, and a decrease in profit, payments, or both to fixed costs.
VER effects on the quota rents. Who receives the quota rents depends on how the government administers the quota.
- If the government auctions the quota rights for their full price, then the government receives the quota rents. In this case, the quota is equivalent to a specific export tax set equal to the difference in prices , shown as the length of the green line segment in Figure 7.36 "Welfare Effects of a VER: Large Country Case".
- If the government gives away the quota rights, then the quota rents accrue to whoever receives these rights. Typically, they would be given to the exporting producers, which would serve to offset the producer surplus losses. It is conceivable that the quota rents may exceed the surplus loss so that the export industry is better off with the VER than without. Regardless, the benefits would remain in the domestic economy.
VER effects on the exporting country. The aggregate welfare effect for the country is found by summing the gains and losses to consumers, producers, and the recipients of the quota rents. The net effect consists of three components: a positive terms of trade effect (c), a negative production distortion (h), and a negative consumption distortion (f).
Because there are both positive and negative elements, the net national welfare effect can be either positive or negative. The interesting result, however, is that it can be positive. This means that a VER implemented by a large exporting country may raise national welfare.
Generally speaking, the following are true:
- Whenever a large country implements a small restriction on exports, it will raise national welfare.
- If the VER is too restrictive, national welfare will fall.
- There will be a positive quota level that will maximize national welfare.
However, it is also important to note that not everyone’s welfare rises when there is an increase in national welfare. Instead, there is a redistribution of income. Consumers of the product and recipients of the quota rents will benefit, but producers may lose. A national welfare increase, then, means that the sum of the gains exceeds the sum of the losses across all individuals in the economy. Economists generally argue that, in this case, compensation from winners to losers can potentially alleviate the redistribution problem.
VER effects on the importing country’s consumers. Consumers of the product in the importing country suffer a reduction in well-being as a result of the VER. The increase in the domestic price of both imported goods and the domestic substitutes reduces the amount of consumer surplus in the market.
VER effects on the importing country’s producers. Producers in the importing country experience an increase in well-being as a result of the VER. The increase in the price of their product increases producer surplus in the industry. The price increases also induce an increase in the output of existing firms (and perhaps the addition of new firms), an increase in employment, and an increase in profit, payments, or both to fixed costs.
VER effects on the importing country. The aggregate welfare effect for the country is found by summing the gains and losses to consumers and producers. The net effect consists of three components: a negative terms of trade effect (C), a negative consumption distortion (D), and a negative production distortion (B).
Since all three components are negative, the VER must result in a reduction in national welfare for the importing country. However, it is important to note that a redistribution of income occurs—that is, some groups gain while others lose. This is especially important because VERs are often suggested by the importing country. This occurs because the importing country’s government is pressured by the import-competing producers to provide protection in the form of an import tariff or quota. Government reluctance to use these policies often leads the importer to negotiate VERs with the exporting country. Although the importing country’s national welfare is reduced, the import-competing producers gain nonetheless.
VER effects on world welfare. The effect on world welfare is found by summing the national welfare effects on the importing and exporting countries. By noting that the terms of trade gain to the importer is equal to the terms of trade loss to the exporter, the world welfare effect reduces to four components: the importer’s negative production distortion (B), the importer’s negative consumption distortion (D), the exporter’s negative consumption distortion (f), and the exporter’s negative production distortion (h). Since each of these is negative, the world welfare effect of the VER is negative. The sum of the losses in the world exceeds the sum of the gains. In other words, we can say that a VER results in a reduction in world production and consumption efficiency.
Key Takeaways
- A VER raises consumer surplus in the export market and lowers it in the import country market.
- A VER lowers producer surplus in the export market and raises it in the import country market.
- National welfare may rise or fall when a large exporting country implements a VER.
- National welfare in the importing country rises when a large exporting country implements a VER.
- A VER of any size will reduce world production and consumption efficiency and thus cause world welfare to fall.
Exercises
-
Jeopardy Questions. As in the popular television game show, you are given an answer to a question and you must respond with the question. For example, if the answer is “a tax on imports,” then the correct question is “What is a tariff?”
- The direction of change of domestic producer surplus when a binding VER is implemented by an exporting country.
- The direction of change of foreign producer surplus when a binding VER is implemented by an exporting country.
- The direction of change of domestic consumer surplus when a binding VER is implemented by an exporting country.
- The direction of change of foreign consumer surplus when a binding VER is implemented by an exporting country.
-
Consider the following trade policy action listed along the top row of the table below. In the empty boxes, use the following notation to indicate the effect of the policy on the variables listed in the first column:
+ the variable increases
− the variable decreases
0 the variable does not change
A the variable change is ambiguous (i.e., it may rise, it may fall)
Use a partial equilibrium model to determine the answers, and assume that the shapes of the supply and demand curves are “normal.” Assume that the policy does not begin with, or result in, prohibitive trade policies. Also assume that the policy does not correct for market imperfections or distortions.
Table 7.16 Effects of a VER Elimination
| Elimination of a Binding VER by a Large Exporting Country | |
|---|---|
| Domestic Market Price | |
| Domestic Industry Employment | |
| Domestic Consumer Welfare | |
| Domestic Producer Welfare | |
| Domestic Government Revenue | |
| Domestic National Welfare | |
| Foreign Price | |
| Foreign Consumer Welfare | |
| Foreign Producer Welfare | |
| Foreign National Welfare |




