This is “Long-Run Determinants of Exchange Rates”, section 18.3 from the book Finance, Banking, and Money (v. 1.1). For details on it (including licensing), click here.
For more information on the source of this book, or why it is available for free, please see the project's home page. You can browse or download additional books there. To download a .zip file containing this book to use offline, simply click here.
18.3 Long-Run Determinants of Exchange Rates
Learning Objectives
- What is purchasing power parity?
- What are the other long-run determinants of exchange rates?
If transaction costs are zero, identical goods should have the same price no matter what unit of account that price is expressed in. Or so says the law of one price. The reason is clear: if they did not, arbitrageurs would buy where the good was cheapest and sell where it was highest until the prices were equalized. Where transaction costs are nontrivial or goods are similar but not identical, we don’t expect a single price, but rather a band or range of prices. So if product X cost $100 in Country Y and $110 in Country Z, and it costs $10 to transport X from Y to Z, there would be no arbitrage opportunity and the price differential could persist. If the price of X rose in Z to $120, we’d expect it to increase in Y to at least $110, or arbitrageurs would start buying it in Y and selling it in Z until the prices were within $10 of each other. Similarly, Japanese-style beer is not the same as U.S.-style beer. But it is close enough that we would not expect the prices to vary widely or otherwise consumers would dump Bud, Miller, and Coors in favor of Kirin and Sapporo (or vice versa, as the case may be).
This sort of analysis has led economists to apply the law of one price to entire economies in what they call the theory of purchasing power parity (PPP), which predicts that, in the long run, exchange rates will reflect price level changes. In other words, higher rates of inflation in Country A compared to Country B will cause Country A’s currency to depreciate vis-à-vis Country B’s currency in the long run. In the short run, however, matters are quite different, as Figure 18.4 "Purchasing power parity, United Kingdom and United States, 1975–2005" shows. If PPP held in the short run, USD should have appreciated against the pound (the blue line should be above zero) every year in which inflation in the United Kingdom exceeded inflation in the United States (the red line is above zero), and vice versa. Clearly, that was not the case. But PPP has the long-run right, in sign but not quite in magnitude. Between 1975 and 2005, prices rose in Great Britain a shade under 205 percent all told. In that same period, they rose just under 142 percent in the United States. In other words, prices rose about 44 percent ([205 − 142]/142) more in Britain than in the United States. Over that same period, the pound sterling depreciated 22 percent against USD (from £.4505 to £.5495 per USD or from $2.22 to $1.82 per £1), just as PPP theory predicts it should have. But why the discrepancy in magnitude?
Figure 18.4 Purchasing power parity, United Kingdom and United States, 1975–2005
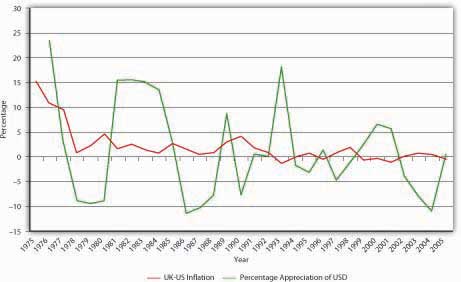
For starters, not all goods and services are traded internationally. Land and haircuts come immediately to mind, but many other things as well when you think about it hard enough. There is no reason for prices of those goods to be the same or even similar in different countries. Arbitrageurs cannot buy low in one place and sell high in another because transaction costs are simply too high. (For example, you could get a great haircut in Malaysia for fifty cents but it would cost several thousand dollars and several days to get there and back.)
Figure 18.5 Determinants of exchange rates in the long run
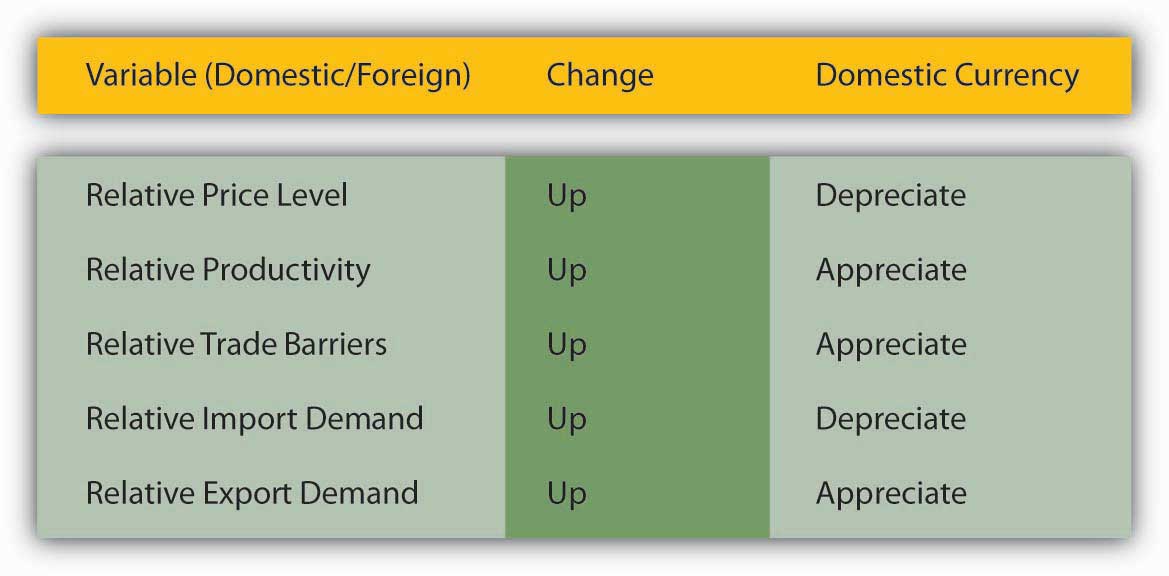
In addition, three other factors affect exchange rates in the long run: relative trade barriers, differential preferences for domestic and foreign goods, and differences in productivity. Tariffs (taxes on imported goods), quotas (caps on the quantity of imported goods), and sundry nontariff barriers (NTBs) to tradehttp://www.wto.org/english/thewto_e/whatis_e/tif_e/agrm9_e.htm increase demand for domestic over foreign goods, thereby allowing the domestic currency to appreciate without injuring sales of domestic goods. Preferences for domestic goods have the same effect; preferences for foreign goods (French wine, German beer, Japanese automobiles) have the opposite effect, depreciating the domestic currency by maintaining demand for foreign goods even in the face of higher prices. Finally, as a country becomes relatively more productive than other countries, the price of its wares tends to fall. Its currency, therefore, appreciates because it can do so without injuring exports. If a country’s productivity lags that of other countries, by contrast, its currency will depreciate. Of course, this is all ceteris paribus. Figure 18.5 "Determinants of exchange rates in the long run" summarizes the discussion.
Key Takeaways
- Purchasing power parity (PPP) is the application of the law of one price to entire economies.
- It predicts that exchange rates will adjust to relative price level changes, to differential inflation rates between two countries. They indeed do, but only in the long run and not to precisely the same degree.
- In the long run, exchange rates are determined by PPP (as described above) and relative differences in productivity, trade barriers, and import and export demand.
- As Country A’s price level and import demand increase, and as Country A’s productivity, trade barriers, and export demand decrease vis-à-vis another Country B, Country A’s currency depreciates and Country B’s appreciates.
- Basically, anything that lowers demand for Country A’s goods, services, and currency induces the currency to depreciate; anything that increases demand for Country A’s stuff induces the currency to appreciate in response.
- Higher inflation relative to Country B makes Country A’s stuff look more expensive, lowering demand and inducing depreciation.
- If economic actors in Country A take a fancy to Country B’s stuff, they will import it even if Country A’s currency weakens, making Country B’s stuff more expensive. Reductions in trade barriers (lower tariffs, higher quotas, fewer NTBs) will exacerbate that.
- If, for whatever reason, economic actors in Country B don’t like Country A’s stuff as much as they used to, they’ll buy less of it unless Country A’s currency depreciates, making it cheaper.
- Finally, if Country A’s productivity slips relative to Country B’s, Country A’s goods and services will get more expensive than Country B’s so it will sell in Country B only if its currency depreciates.




